Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
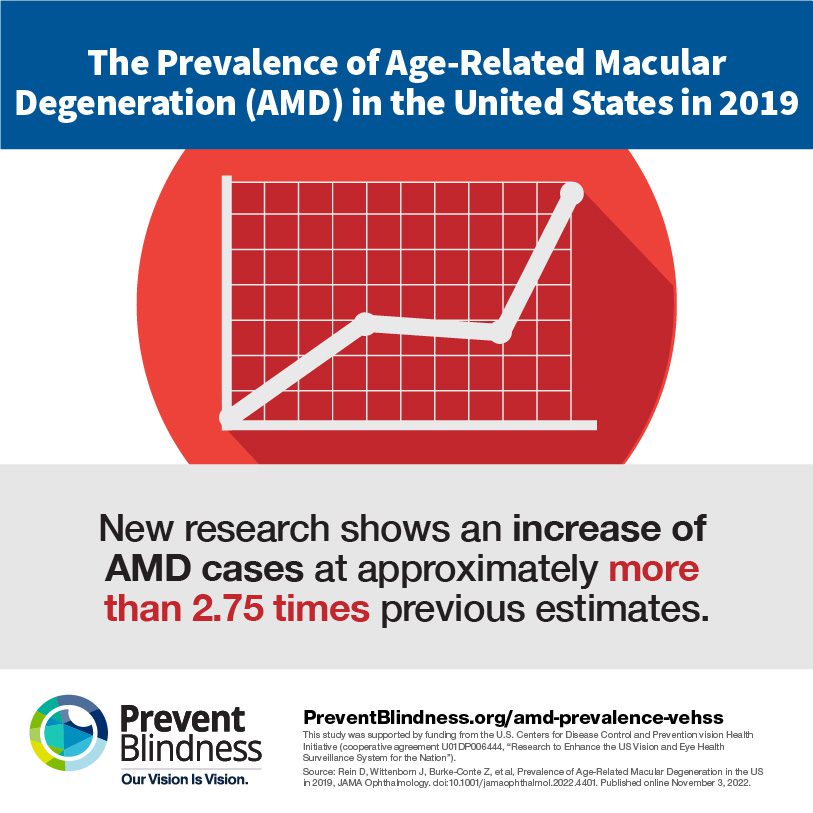
A 2022 study The Prevalence of Age-Related Macular Degeneration in the United States In 2019, found that, in 2019, an estimated 19.83 million Americans were living with some form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). This is an increase of approximately more than 2.75 times previous estimates (which used a more conservative definition of early AMD based on larger drusen size).
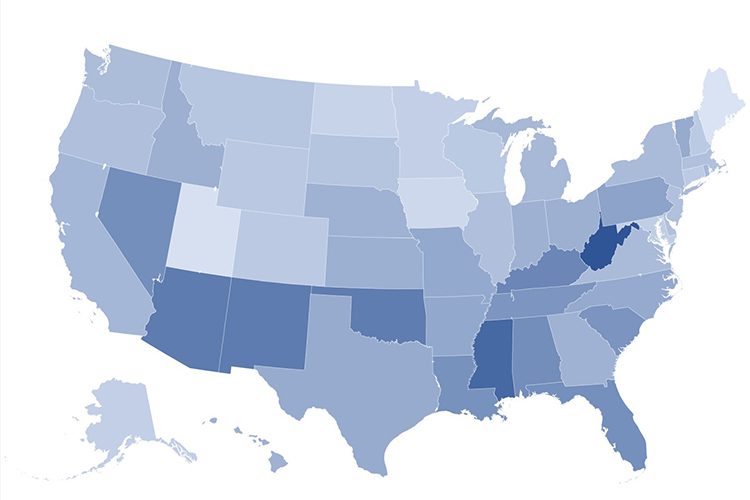
An estimated 18.34 million Americans had early AMD and 1.49 million had the late stage vision threatening form of AMD (“late AMD” included geographic atrophy in this study). In addition to national prevalence data, the new study also provides data at the state and county level.
Additional key findings from the study include:
- Approximately one in 10 Americans aged 50 and older have the early form of AMD and approximately 1 out of every 100 Americans ages 50 and older have the vision threatening late form of AMD.
- Among persons aged 80 and older, approximately 3 in 10 had early AMD, and approximately 1 and 10 have the vision threatening late form of AMD.
- Gender, and age-standardized rates of the disease were lowest for Black Americans as compared to other race/ethnicity groups.
- The prevalence of both early and late AMD varied widely by U.S. county. After standardizing by gender and race/ethnicity, rates for vision threatening AMD were the highest in the Midwest and New England regions of the country, and in Florida.